- Finerenone in Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Diabetic Kidney Disease. The FIDELIO-DKD clinical trial is summarized in this simple infographic.
Rationale and Clinical Equipoise
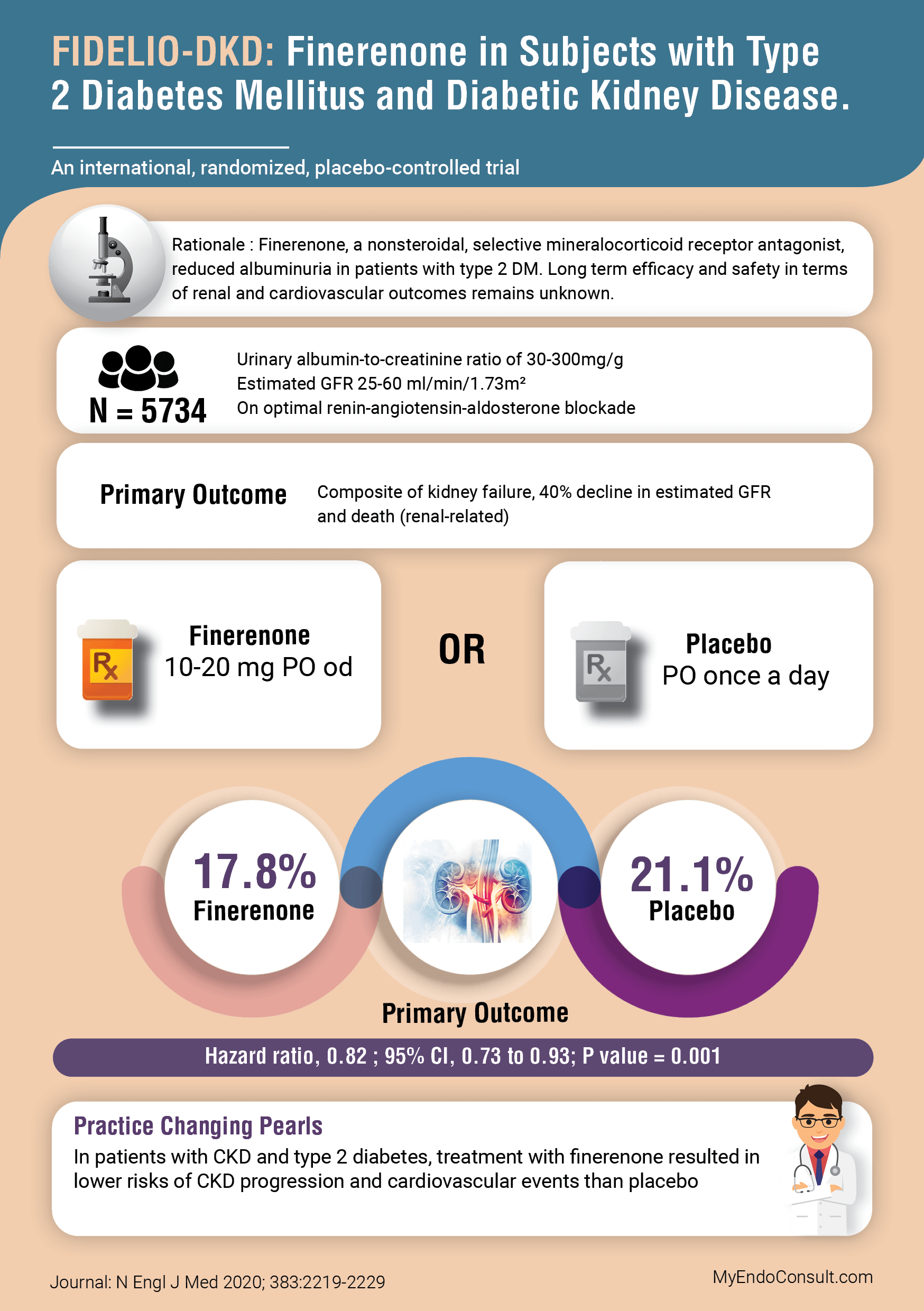
Finerenone, a nonsteroidal, selective mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, reduced albuminuria in patients with type 2 DM. Long term efficacy and safety in terms of renal and cardiovascular outcomes remains unknown.
Study Design
- A multicenter, double-blind, randomized controlled trial
- 2833 subjects were randomized to the intervention (Finerenone) arm and 2841 to the placebo arm.
- An intention-to-treat analysis
- Median follow-up 2.6 years
- Variable doses of finerenone, based on the patient’s baseline estimated GFR. If eGFR > 60 (20mg daily), estimated GFR 25-60 (10mg daily with an increased in dose to 20mg after 1 month)
Study Eligibility Criteria
- Age >18 years with a diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio of 30-300mg/g
- Estimated GFR 25-60 ml/min/1.73m²
- On optimal renin-angiotensin-aldosterone blockade
- Serum potassium less than 4.8 mEq
- On at least 2 contraceptives if a female of child-bearing age.
Primary Outcome
Composite of kidney failure, 40% decline in estimated GFR and death (renal-related). Comparison of finerenone versus placebo ; 17.8% versus 21.1% (Hazard ratio, 0.82 ; 95% CI, 0.73 to 0.93; P value = 0.001)
Secondary Outcomes
- Death from cardiovascular causes, nonfatal myocardial infarction, nonfatal stroke,or hospitalization for heart failure
- Comparison of finerenone vs placebo; 13.0% vs 14.8% (Hazard Ratio, 0.86; 95% CI 0.75-0.99; P=0.03)
- Death from any cause
- Comparison of finerenone vs placebo; 7.7% vs 8.6% (HR 0.90; 95% CI 0.75-1.07; P=0.02)
Critical Appraisal
Patients with nonalbuminuric chronic kidney disease and CKD in the absence of diabetes were excluded, thus limiting the generalizability of the findings.
Practice Changing Pearls (Conclusion)
- In patients with CKD and type 2 diabetes, treatment with finerenone resulted in lower risks of CKD progression and cardiovascular events than placebo.
- Involvement of the study sponsor in the design, conduct and analysis of the study is a significant limitation. A single site was also excluded due to violations of Good Clinical Practice guidelines.
References
- Bakris GL et al; FIDELIO-DKD Investigators. Effect of Finerenone on Chronic Kidney Disease Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2020 Dec 3;383(23):2219-2229. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2025845.
Kindly Let Us Know If This Was helpful? Thank You!